안녕하세요? 이번 글은 래스터 데이터의 범위 내에서 지정된 개수의 무작위 샘플 지점을 생성하는 코드 예제를 소개해 보겠습니다. 해당 코드는 Python용 종 분포 모델링(SDM: Species Distribution Modeling) 도구, elapid(엘라피드)의 일부 소스 코드를 QGIS Python 콘솔에서 동작하도록 수정한 것입니다.
elapid(엘라피드): Python용 종 분포 모델링 도구 소개
안녕하세요? 이번 글은 Python용 종 분포 모델링(SDM: Species Distribution Modeling) 도구, elapid(엘라피드)에 관해 간략히 소개해 보겠습니다. elapid의 개발자는 플래닛 랩스 지구관측연구소(Earth Observation La
foss4g.tistory.com
먼저, 필요한 패키지를 호출합니다.
import numpy as np
import geopandas as gpd
from osgeo import gdal
from qgis.core import QgsRasterLayer, QgsRectangle
from shapely.geometry import Point
아래 함수는 입력으로 주어진 래스터 파일을 열고 첫 번째 밴드 데이터를 불러온 후, 래스터의 공간 변환 정보와 크기를 추출합니다. 지정된 nodata 값이 있을 경우 이를 사용하여 해당 값을 제외하는 마스크를 생성하며, ignore_mask 옵션이 활성화되면 마스크를 무시하고 전체 래스터에서 샘플링합니다.
그리고 유효한 픽셀의 인덱스를 마스크를 기반으로 추출한 후, 요청된 샘플 개수만큼 무작위로 선택합니다. 선택된 픽셀 인덱스는 래스터의 공간 변환 정보를 사용하여 지리적 좌표로 변환되고, 변환된 좌표를 기반으로 좌표 체계를 설정한 GeoSeries 객체를 생성하여 반환합니다.
def sample_raster(
raster_path: str, count: int, nodata: float = None, ignore_mask: bool = False
) -> gpd.GeoSeries:
"""Create a random geographic sample of points based on a raster's extent.
Args:
raster_path: raster file path to sample locations from
count: number of samples to generate
nodata: add pixels with this value to the nodata mask
ignore_mask: sample from the full extent of the raster instead of unmasked areas only
Returns:
points: Point geometry geoseries
"""
# Open the raster using gdal
raster = gdal.Open(raster_path)
if raster is None:
raise ValueError(f"Unable to open raster: {raster_path}")
band = raster.GetRasterBand(1)
transform = raster.GetGeoTransform()
cols = raster.RasterXSize
rows = raster.RasterYSize
if nodata is not None:
nodata_value = band.GetNoDataValue()
if nodata_value is None:
nodata_value = nodata
data = band.ReadAsArray()
mask = data != nodata_value
else:
mask = np.ones((rows, cols), dtype=bool)
if ignore_mask:
mask = np.ones((rows, cols), dtype=bool)
# Get indices of valid pixels
valid_indices = np.column_stack(np.where(mask))
if len(valid_indices) < count:
raise ValueError(
"The number of valid pixels is less than the requested sample count."
)
# Randomly sample indices
sampled_indices = valid_indices[
np.random.choice(valid_indices.shape[0], count, replace=False)
]
# Convert pixel indices to geographic coordinates
sampled_points = []
for row, col in sampled_indices:
x = transform[0] + col * transform[1] + row * transform[2]
y = transform[3] + col * transform[4] + row * transform[5]
sampled_points.append(Point(x, y))
# Create GeoSeries with sampled points
spatial_ref = raster.GetSpatialRef()
if spatial_ref is not None:
crs = spatial_ref.ExportToWkt()
else:
crs = None
points = gpd.GeoSeries(sampled_points, crs=crs)
return points
이전 글에서 생성한 NDVI 분광지수 이미지 범위 내에서 10,000개의 무작위 샘플 지점을 생성해 보겠습니다. 이때 nodata 값은 0이고 ignore_mask 옵션은 비활성화 상태이므로, 0 값을 제외하는 마스크를 기반으로 유효한 픽셀의 인덱스를 추출한 후, 10,000개 샘플 지점을 무작위로 선택합니다.
PyQGIS: KOMPSAT-3 위성영상 분광지수 이미지 생성 코드 예제
안녕하세요? 이번 글은 PyQGIS를 통해 KOMPSAT-3 위성영상의 분광지수 이미지를 생성하는 코드 예제를 제공해 봅니다. QGIS 메뉴 바에서 "플러그인 > 파이썬 콘솔"에서 실행해보시면 되겠습니다. 먼저
foss4g.tistory.com
# Example usage in QGIS Python Console
output_dir = "D:/kari_sdm/data/white_naped_crane/environmental_variables"
raster_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "NDVI.tif")
samples = sample_raster(raster_path, count=10_000, nodata=0, ignore_mask=False)
print(samples.head())0 POINT (472773.824 3912674.464)
1 POINT (459809.824 3908228.064)
2 POINT (464813.424 3915026.464)
3 POINT (466238.624 3906954.064)
4 POINT (470284.624 3904593.664)
dtype: geometry
QGIS 프로젝트에 배경 샘플 레이어를 추가하고 시각적으로 스타일을 설정하는 함수를 정의합니다. GeoSeries 객체를 기반으로 메모리 레이어를 생성하며, 이를 지정된 이름과 스타일 속성으로 QGIS 프로젝트에 추가합니다.
def add_background_layer(
geoseries: gpd.GeoSeries,
layer_name="Background",
color="red",
opacity=0.5,
size=1.0,
):
"""Add a background sample layer to QGIS project.
Args:
geoseries: GeoSeries containing the background points
layer_name: Name of the layer to add to QGIS project
color: Color of the points
opacity: Opacity of the points
size: Size of the points
"""
# Create a memory layer from GeoSeries
vl = QgsVectorLayer(
"Point?crs={}".format(geoseries.crs.to_string()), layer_name, "memory"
)
pr = vl.dataProvider()
# Add fields and features to the layer
pr.addAttributes([QgsField("id", QVariant.Int)])
vl.updateFields()
for idx, point in enumerate(geoseries):
if not point.is_empty:
feature = QgsFeature()
feature.setGeometry(QgsGeometry.fromWkt(point.wkt))
feature.setAttributes([idx])
pr.addFeature(feature)
vl.updateExtents()
# Style the layer
symbol = QgsSymbol.defaultSymbol(vl.geometryType())
symbol.setColor(QColor(color))
symbol.setOpacity(opacity)
symbol.setSize(size)
renderer = QgsSingleSymbolRenderer(symbol)
vl.setRenderer(renderer)
# Add layer to QGIS project
QgsProject.instance().addMapLayer(vl)
print(f"Layer '{layer_name}' added and styled successfully!")
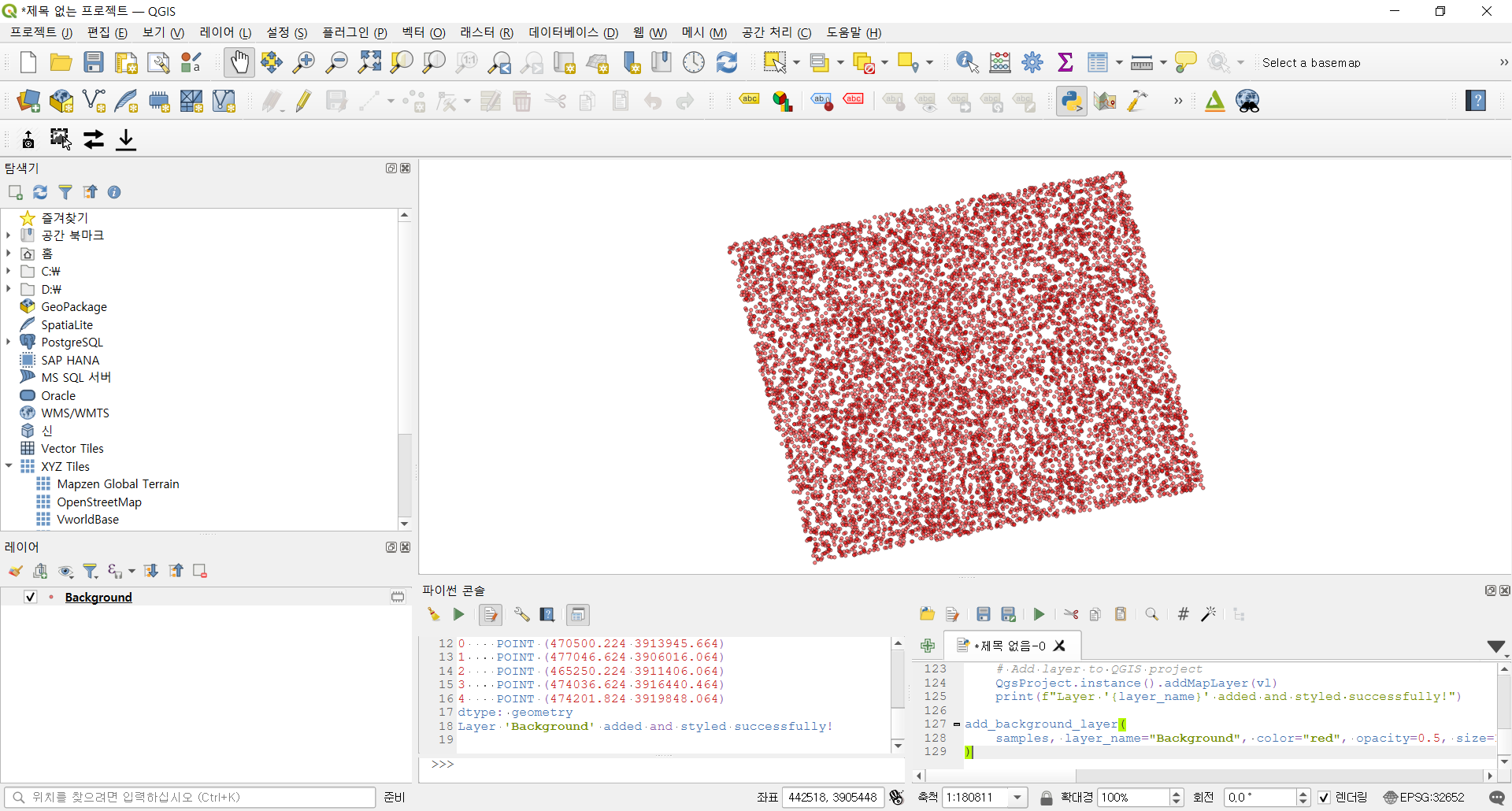
이제 지정된 스타일 속성을 가진 배경 샘플 레이어를 생성하고 추가합니다. 결과는 다음과 같습니다.
add_background_layer(
samples, layer_name="Background", color="red", opacity=0.5, size=1.0
)